Non-Invasive Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Decreases Heart Rate Variability Independent of Caloric Load
Kristen Sparrow • March 16, 2025

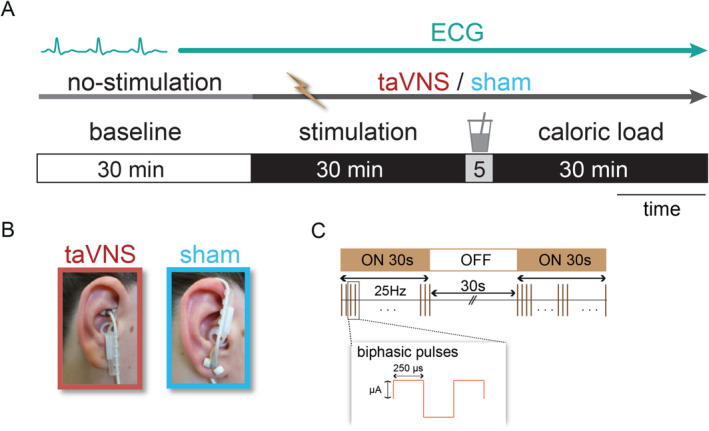
In this study, the authors looked at the effect of TAVNS comparing right and left sides. They found no difference between the two sides in the cardiac effects. HOWEVER! They found that TAVNS DECREASED HRV leading to arousal. This is in contradistinction to most studies which show an increase in HRV. The researchers used the cymba concha for stimulation at 25 hz intermittent, which is almost exactly the protocol I use. (see graphic below)
We’ve discussed TAVNS frequently on the blog, here, and here.
Clearly, there is more to learn about this potential therapy!
Non-Invasive Auricular Vagus Nerve Stimulation Decreases Heart Rate Variability Independent of Caloric Load
- PMID: 40007175
- PMCID: PMC11862327
- DOI: 10.1111/psyp.70017
Abstract
The vagus nerve is crucial in regulating physiological functions, including the cardiovascular system. While heart rate (HR) and its variability (HRV) may provide non-invasive proxies of cardiac vagal activity, transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) has yielded mixed effects, with limited research on right branch stimulation. In a randomized crossover study with 36 healthy participants, we investigated taVNS effects on HR and HRV indexed by SDRR, RMSSD, HF-HRV, and LF/HF ratio. To assess the impact of the stimulation side (left vs. right ear) on cardiovascular indices and interaction with the physiological state, we recorded electrocardiograms in four sessions per person, covering three session phases: baseline, during stimulation (taVNS vs. sham), and post-milkshake consumption with stimulation. First, we found moderate evidence against taVNS affecting HR (BF10 = 0.21). Second, taVNS decreased HRV (multivariate p = 0.004) independent of physiological state, with strong evidence for RMSSD (BF10 = 15.11) and HF-HRV (BF10 = 11.80). Third, taVNS-induced changes were comparable across sides and stronger than sham, indicating consistent cardiovascular effects independent of the stimulation side. We conclude that taVNS reduces HRV as indexed by RMSSD, HF-HRV, and SDRR without altering HR, contradicting the assumption that taVNS per se increases cardiovagal activity as indexed by increased HRV due to stimulating vagal afferents. Instead, our results support the role of vagal afferent activation in arousal. Crucially, taVNS on both sides can safely modulate the cardiovascular system without increasing the risk of bradycardia or causing adverse events in healthy participants, offering new treatment possibilities.
Keywords: ECG; autonomic nervous system; cardiac vagal activity; milkshake; taVNS.